
Typically a coloboma appears oval- or comet-shaped with round end towards the centre. Įye abnormalities have been shown to occur in over 90% of children with fetal alcohol syndrome.
Coloboma is part of a set of characteristic facies that features craniofacial malformations, such as downslanting eyes, ear anomalies, or hypoplasia of zygomatic bone and jaw (micrognathia). Treacher Collins syndrome, autosomal dominant syndrome caused by mutation of TCOF1.

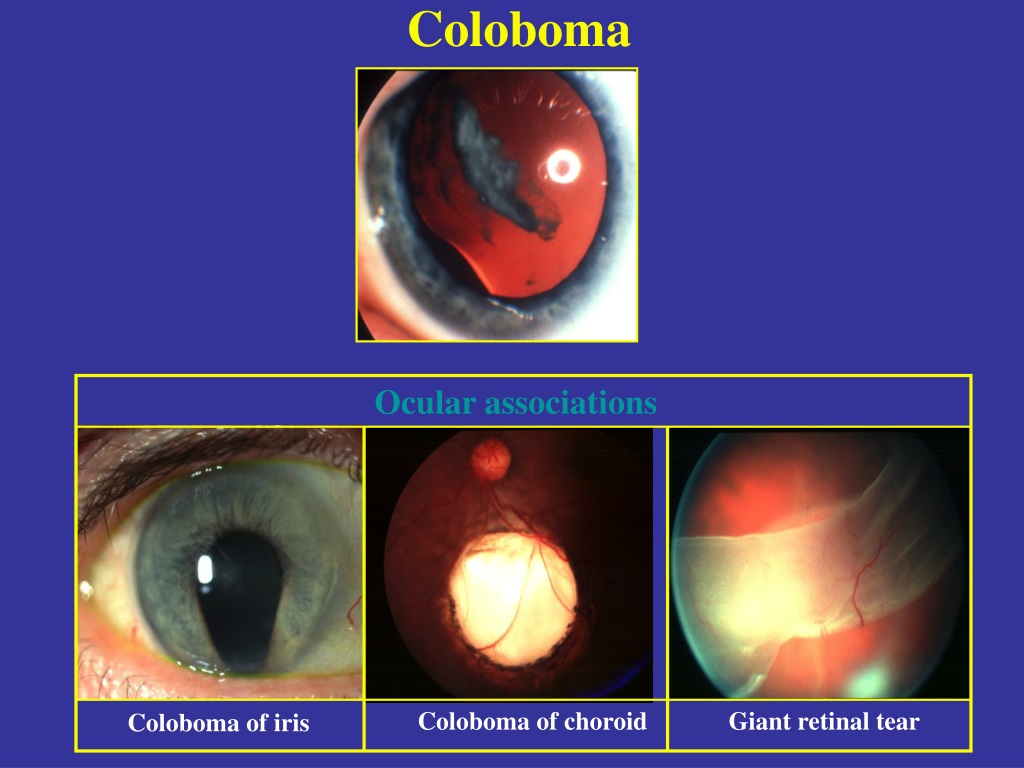
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13), a chromosomal abnormality that can cause a number of deformities, some of which include structural eye defects, including microphthalmia, Peters anomaly, cataract, iris and/or fundus coloboma, retinal dysplasia or retinal detachment, sensory nystagmus, cortical visual loss, and optic nerve hypoplasia.The term "cat eye" was coined because of the particular appearance of the vertical colobomas in the eyes of some patients. Cat eye syndrome, caused by the short arm (p) and a small section of the long arm (q) of human chromosome 22 being present three (trisomic) or four times (tetrasomic) instead of the usual two times.Although these features are no longer used in making a diagnosis, the name has remained. The letters stand for: coloboma of the eye, heart defects, atresia of the nasal choanae, retardation of growth and/or development, genital and/or urinary abnormalities, and ear abnormalities and deafness. CHARGE syndrome, a term that came into use as an acronym for the set of unusual congenital features seen in a number of newborn children.Other ocular malformations that include coloboma or are related to it: Glaucoma, nystagmus, scotoma, or strabismus may also occur. Sometimes, the eye may be reduced in size, a condition called microphthalmia. Other conditions can be associated with a coloboma. Commonly posterior colobomata affect the inferior retina, with resultant deficit in the superior visual field. If, for example, only a small part of the iris is missing, the vision may be normal when a large part of the retina or (especially) optic nerve is missing, the vision may be poor. Visual effects may be mild to more severe depending on the size and location of the coloboma. The pupil cannot contract to a smaller size than pictured, but may still be able to dilate in low light. Iris coloboma in the right eye of a 10-month-old child.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
