
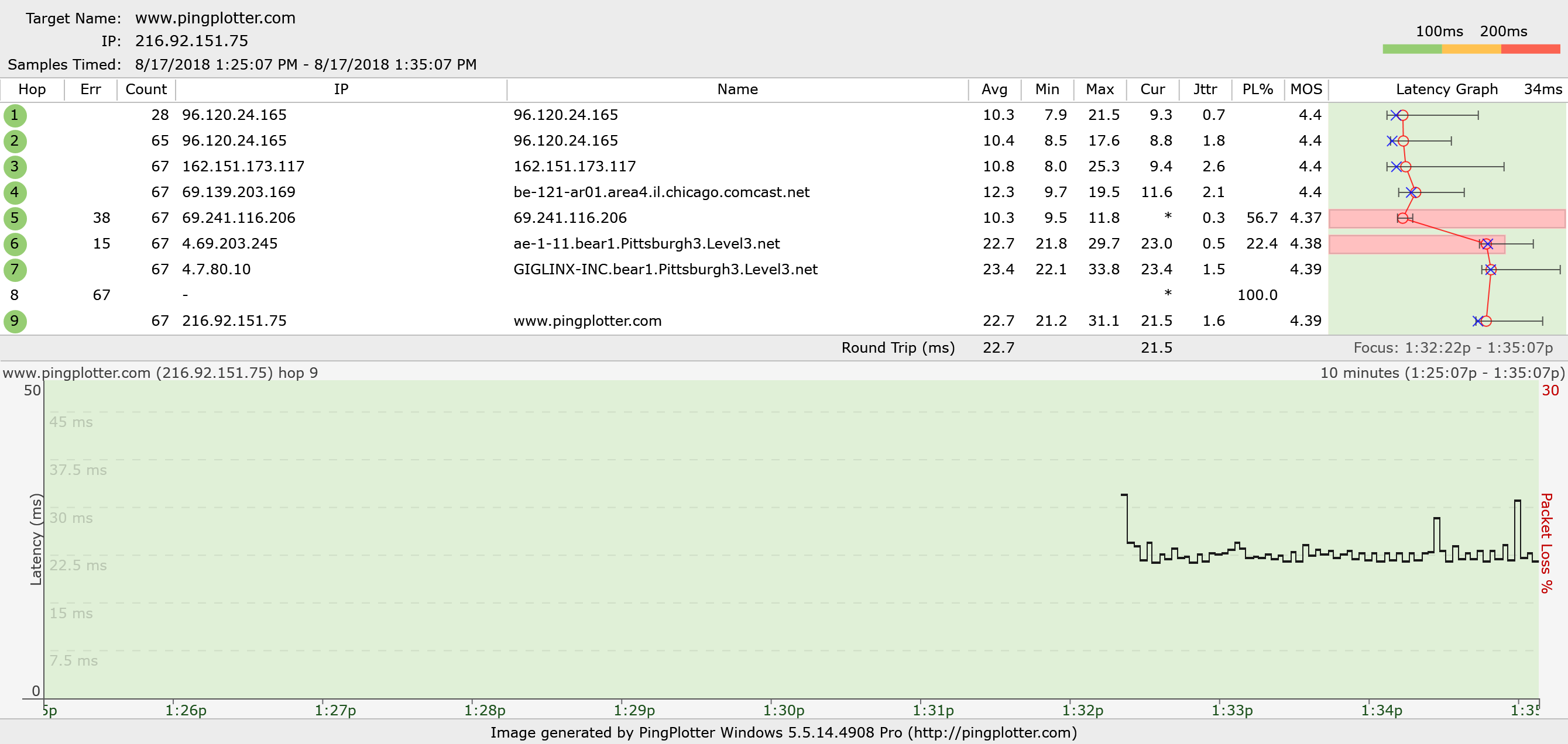

This requires Administrative user rights and, on most operating systems, also requires the installation of a helper library such as Npcap. TCP is the protocol used for all web browsers in addition to FTP, Telnet, and others. If a firewall is blocking ICMP packets, it’s sometimes possible to get a response using TCP packets instead. This method gives you the opportunity to send TCP packets.
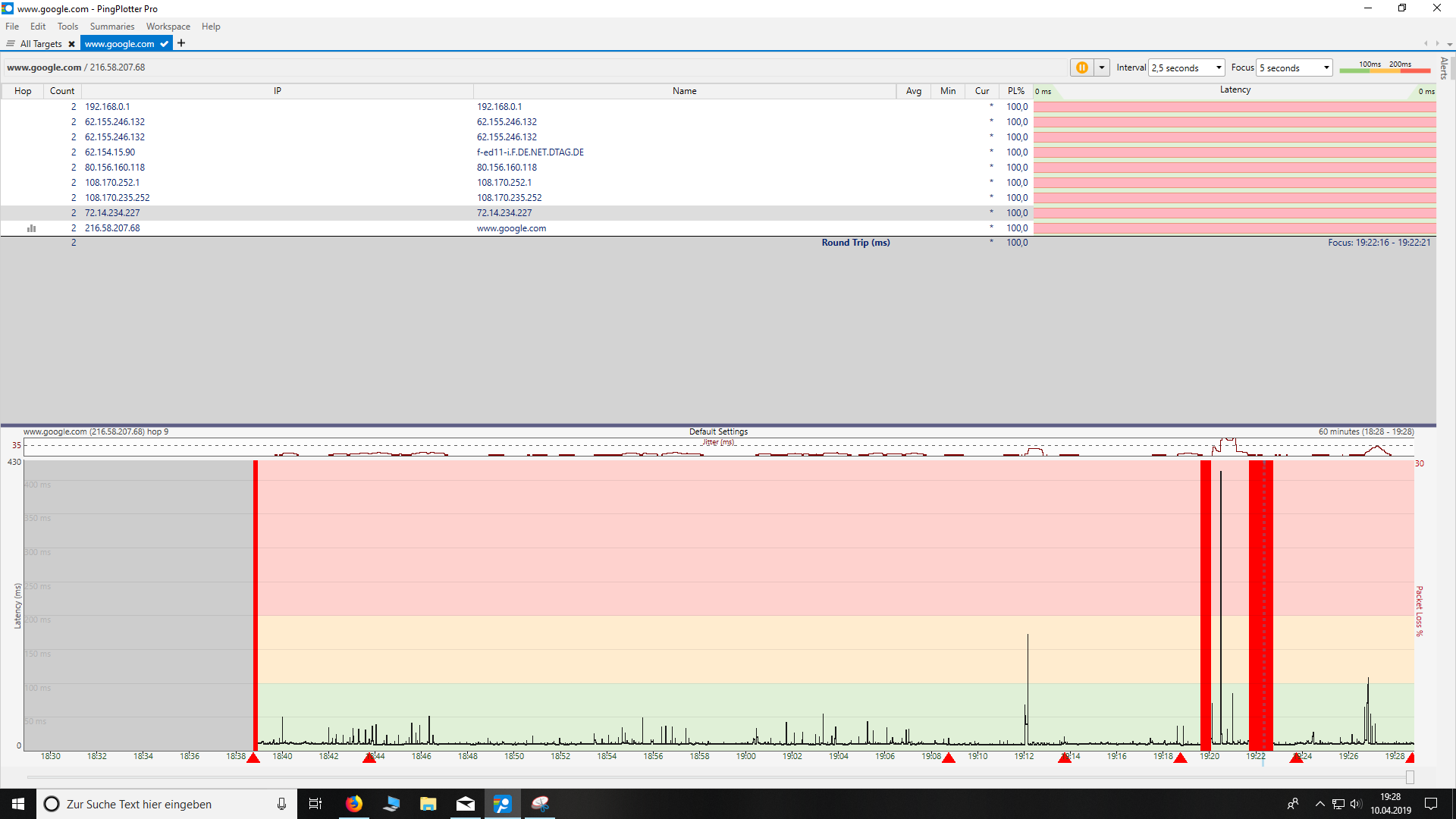
This requires administrative rights, and doesn't work reliably on Windows Vista or newer (including Windows 8). Though not the cure-all for "Destination Unreachable" issues, this is worth a try, especially if you’re getting erratic packet loss or unreachable destination. This method will sometimes allow you to trace to a destination that isn’t reachable via ICMP, or might allow you to reach the internet even if your ISP is blocking ICMP echo requests. This uses ports 33434 – 33500 and closely mirrors Unix’s traceroute command. This requires administrative rights and doesn't work reliably on Windows Vista or newer (including Windows 8). PingPlotter can compose its own ICMP packets - although in most cases this is no more reliable or better than ICMP.DLL. In some rare cases, the standard Windows method doesn't work. ICMP using Raw Sockets (advanced use only).This method does not require administrative rights, and should be the first choice for most users.
PINGPLOTTER AUTO SAVE MANUAL
This method will automatically do manual timings on less-than-accurate operating systems to attempt to get accuracy to 1ms. This is reliable with the least CPU usage (on most operating systems). It works on all Windows operating systems, and is a good balance of reliability and capability. This method is the traditional method and matches the data that the Windows TRACERT command uses. The "Packet Type" settings allows you to pick what kind of data you want to send to tailor PingPlotter to your network needs. The "Engine" settings control what and how PingPlotter sends data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
